Below are the full IP blocks we've been allocated from internet registries such as RIPE.
| Registry | Prefix | Owner |
|---|---|---|
| RIPE | 2a07:e00::/29 | Privex Inc. (AS210083) |
| RIPE | 185.130.44.0/22 | Privex Inc. (AS210083) |
| RIPE | 121.127.33.0/24 | Privex Inc. (AS210083) |
| RIPE | 199.231.235.0/24 | Privex Inc. (AS210083) |
| RIPE | 202.181.177.0/24 | Privex Inc. (AS210083) |
We split this IP space up into smaller blocks, below is a rough guide to how we're using our current allocations:
| Location Used | Prefix | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sweden | 185.130.44.0/24 | Sweden IP Space |
| Sweden | -> 185.130.44.0/27 | Privex Corporate Usage |
| Sweden | 185.130.45.0/24 | Sweden IP Space (2nd /24) |
| Worldwide | 2a07:e00::/32 | Reserved for Privex Corporate Usage |
| Stockholm, Sweden | -> 2a07:e00::/48 | Privex Corporate Usage (used in Kista DC) |
| Worldwide | -> 2a07:e00:ff::/48 | Point-to-point connections (routers, switches etc.) |
| Sweden | 2a07:e01::/32 | General Sweden Usage (primarily customer delegation) |
| Stockholm, Sweden | -> 2a07:e01::/44 (estd.) | Primarily Customers in our Kista Datacenter |
| Fremont, CA, USA | 2a07:e04::/36 | Primarily Customers in our Fremont, CA Datacenter(announced via AS400587) |
| Chicago, IL, USA | 2a07:e05::/36 | Primarily Customers in our Chicago, IL Datacenter(announced via AS400587) |
While information about our BGP communities isn't very useful outside of Privex, it can help when trying to sift through our routing table on our route server.
For example, you can use show ip bgp community 0:201 to see all the IPv4 routes we're receiving from SOL-IX's Route Server.
0:100 - PVX-TRANSIT - All transit BGP routes
0:101 - PVX-TRANSIT-OBE - Transit routes from OBE
0:200 - PVX-PEER - ALL incoming peering prefixes
0:201 - PVX-PEER-SOLIX - SOL-IX peering prefixes only
0:250 - PVX-PEER-DIRECT - Direct BGP peering only
0:300 - PVX-CUST - Our own prefixes
On our physical network for AS210083 where we have control over the networking - we both sign our prefixes using RPKI ROA's, and validate/filter incoming prefixes from our BGP peers. We sign our prefixes by enabling ROA's on RIPE's RPKI Dashboard for all of our IPv4 and IPv6 prefixes, with exact prefix sizes.
We validate/filter incoming prefixes from our peers - whether direct BGP peering or from route servers, using the open source (Rust) RPKI validator service Routinator 3000.
For reference, here are what the different RPKI states mean:
Some networks choose to completely drop any prefixes which are invalid - however, some peers may occasionally misconfigure their RPKI, which could cause a lot of problems if we suddenly had to reject a large amount of prefixes from a large network.
To be safe, we have a scaling local preference based on the RPKI status of each prefix, along with where the prefix came from (SOL-IX route server, STHIX route server, or a direct BGP peer etc.). Prefixes which have invalid RPKI are treated equally with the low local preference of 50 - while valid and not-found have a varying local preference depending on the source of the prefix.
| Peering Profile | RPKI Status | Local Preference | Communities |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOL-IX Route Server | Valid | 200 | 0:200, 0:201 |
| SOL-IX Route Server | RPKI not found | 110 | 0:200, 0:201 |
| SOL-IX Route Server | INVALID | 50 | 0:200, 0:201 |
| STHIX Route Server | Valid | 190 | 0:200, 0:202 |
| STHIX Route Server | RPKI not found | 105 | 0:200, 0:202 |
| STHIX Route Server | INVALID | 50 | 0:200, 0:202 |
| Standard direct BGP peer | Valid | 210 | 0:200, 0:250 |
| Standard direct BGP peer | RPKI not found | 120 | 0:200, 0:250 |
| Standard direct BGP peer | INVALID | 50 | 0:200, 0:250 |
We operate a public route server using Quagga, which works similarly to Hurricane Electric's route server (route-server.he.net).
You can connect to our route server via either SSH, or Telnet, allowing you to browse our Sweden network routing, including the prefixes we receive from our peers.
ssh rs@route-server.privex.io
telnet route-server.privex.io
Above are screenshots of the route server after logging in, via both SSH and Telnet.
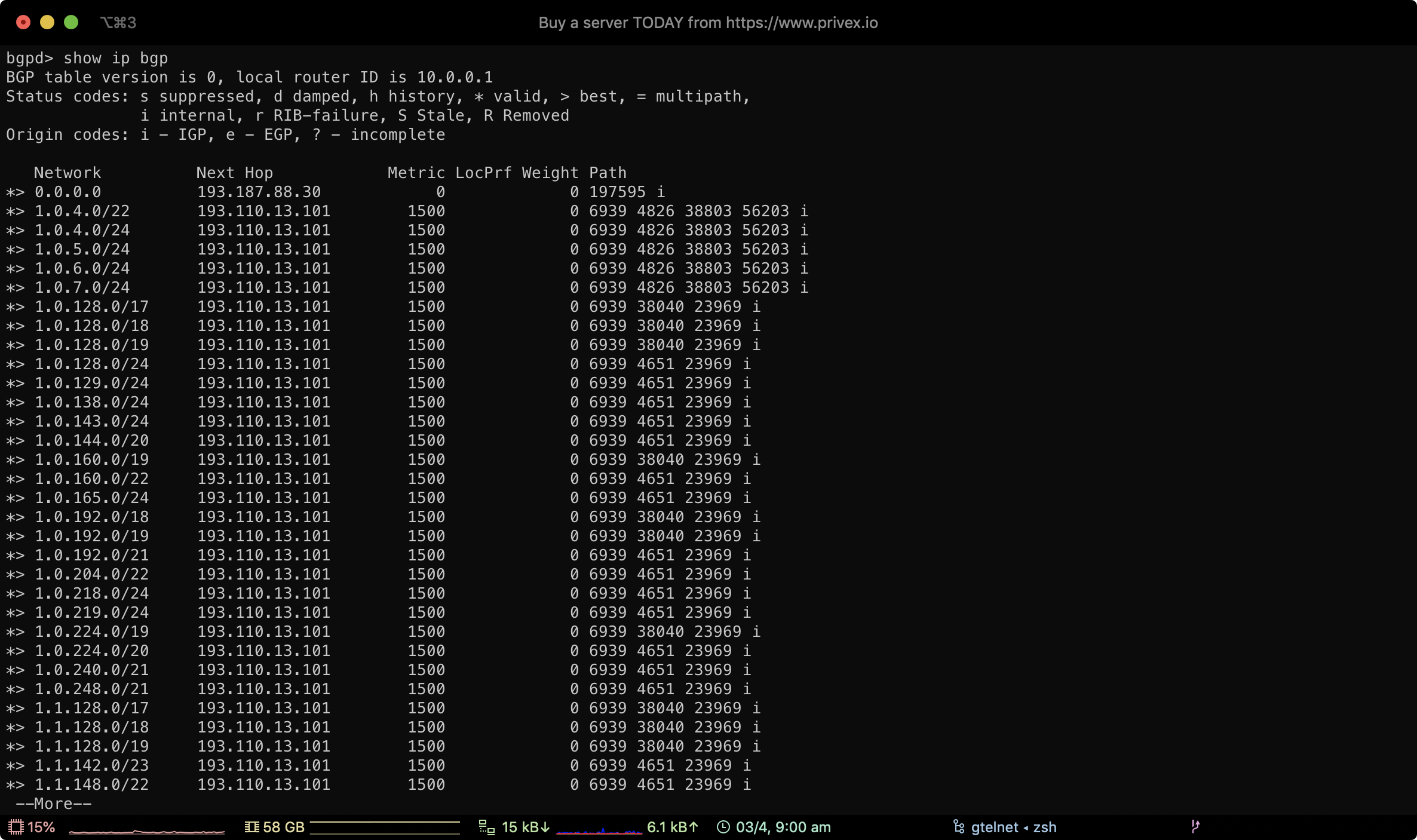
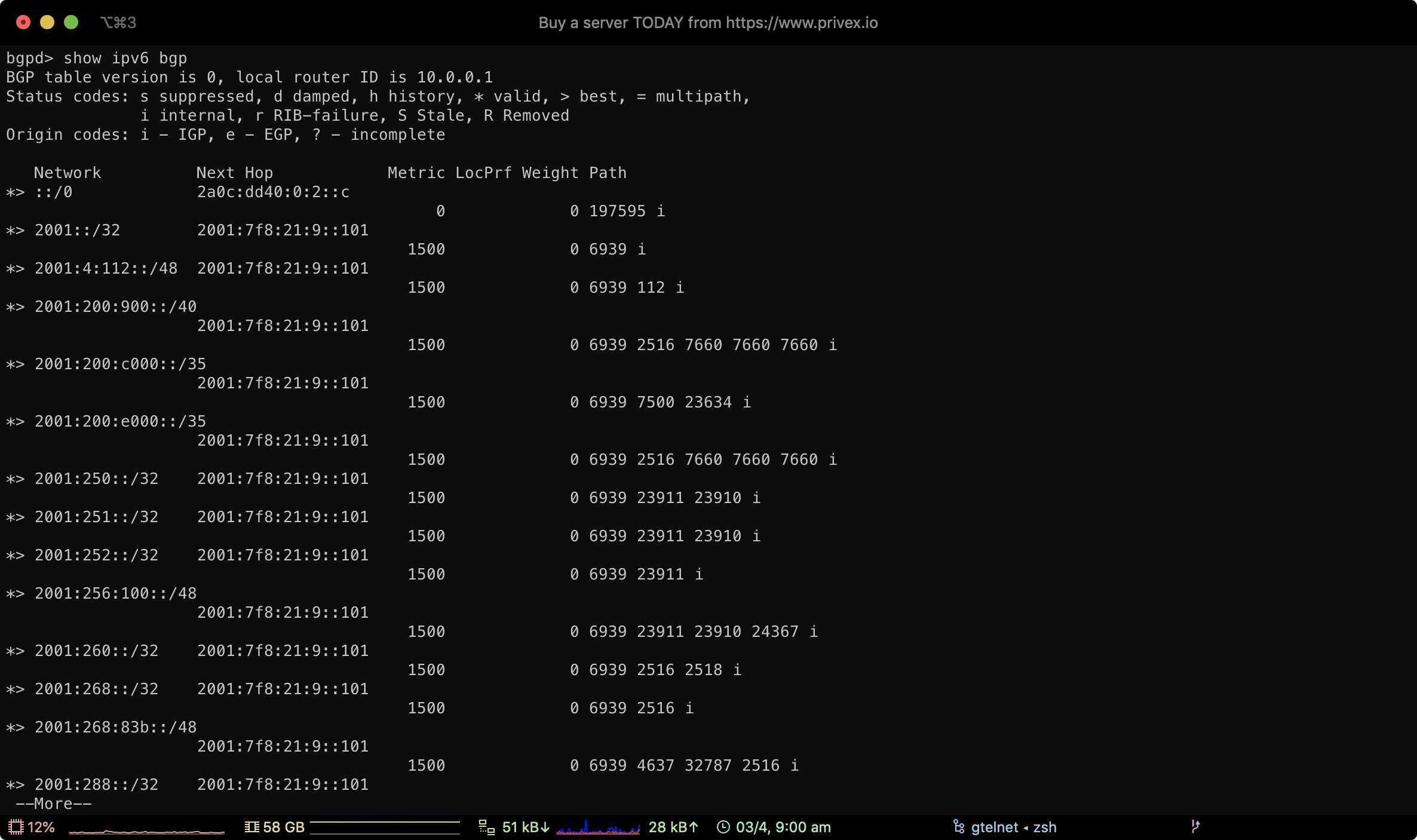
Using the route server commands show ip bgp and show ipv6 bgp, you can view all routing prefixes that our core router knows.
If you type: ? - you'll see various commands available.
You can also type ? after any command to view the sub-commands / options you can use. For example show ip ? or show ipv6 ?
Our BGP prefixes are organised under the community 0:300
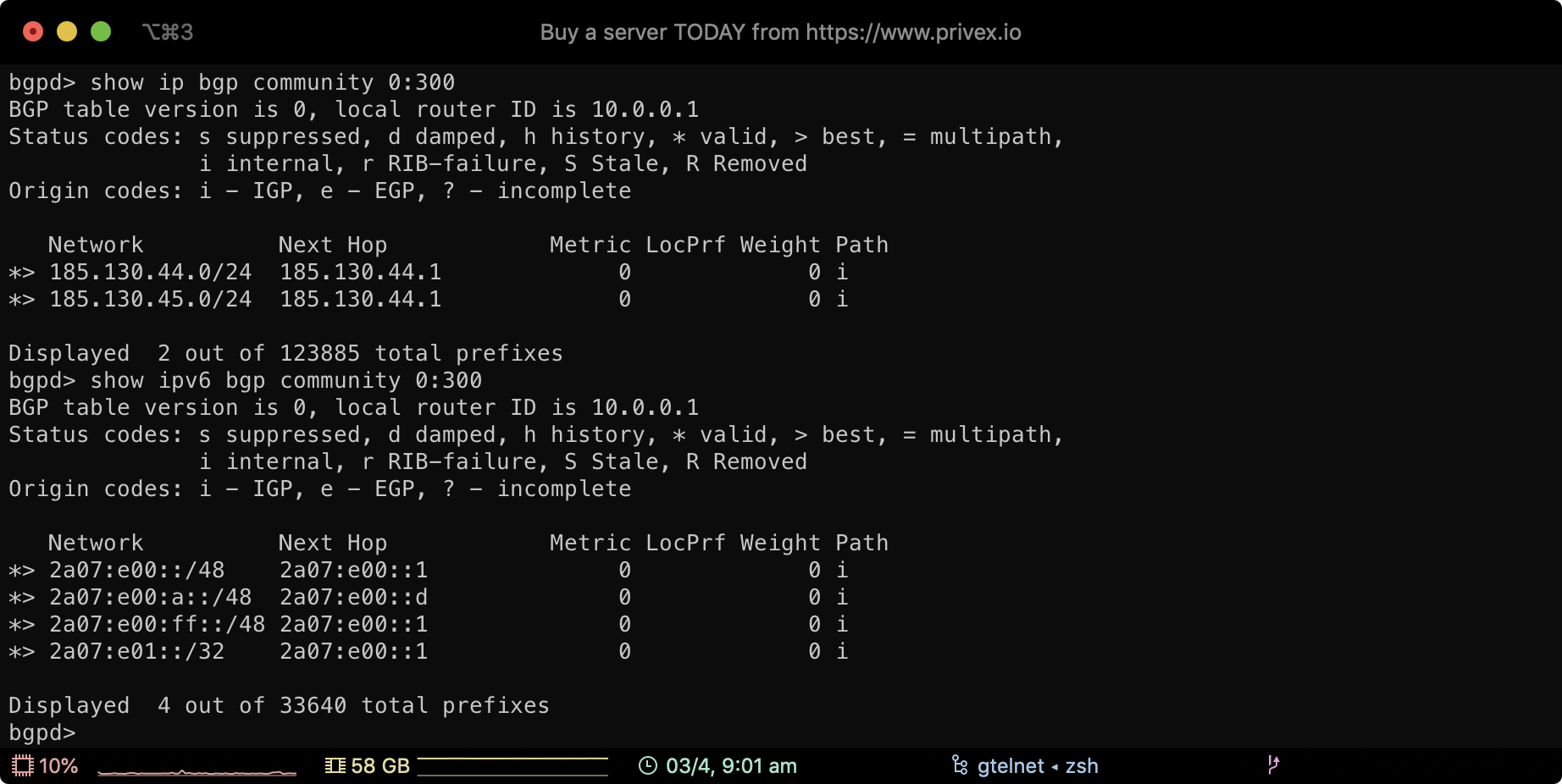
As shown in the screenshot above, you can view the prefixes we're advertising to our peers, by typing:
show ip bgp community 0:300
show ipv6 bgp community 0:300
This will show the IPv4 and the IPv6 prefixes we're advertising, along with their next hop IP address (which IP handles that prefix)
See our BGP Communities section to view the other communities we organise our routes with.
Show all IPv4 prefixes we're receiving from AS 6939 (Hurricane Electric), including prefixes they're advertising for third parties (e.g. they're acting as transit for that ASN)
show ip bgp regexp ^6939
Show all IPv4 prefixes which are direct to AS6939 (no third-party routes they advertise)
show ip bgp regexp ^6939$
Show only internal IPv4 BGP prefixes (empty ASN path), which generally means prefixes that we're advertising ourselves.
show ip bgp regexp ^$
Show all IPv6 prefixes that have the ASN 13335 (Cloudflare) in their path. This will include routes that we're not receiving from AS13335, instead they're routes which include a hop via Cloudflare AS13335.
show ipv6 bgp regexp 13335
Show all IPv6 prefixes we're receiving from AS 13335 (Cloudflare), including routes they're advertising for a third party which they're acting as transit for/
show ipv6 bgp regexp ^13335